| GPS Flight Assistance and Autopilot The GPS Navigation Control board is a key component and provides an autopilot the can control the position and course of the copter. It provides a Position Hold and Come Home feature, as well as the capability for autonomous flight between waypoints. | ||
| Position hold | ||
| ComingHome With the flick of a switch on your transmitter, the Navigation and Flight controllers make the copter climb up to a preset height, and fly it directly back to the take-off position. | ||
| Dynamic Position Hold Even while the Navigation Control board is in Position Hold you can “fly” the set point position and this allows you to fly the copter in a straight line even when it is windy – a great feature for shooting tracking video shots. | ||
| Weather conditions | ||
| Automatic takeoff, waypoint flying and landing | ||
| Redundant Flight Control Systems | ||
| Waypoint Flying | ||
| Automatic Panoramas With the flick of a switch on the RC transmitter, the copter can automatically take a panorama, rotating and tilting the camera to create a mosaic of appropriately overlapped images that can be stitched together like this to form a beautiful . Beautiful panoramas can be created like this example. | ||
Inverse Panorama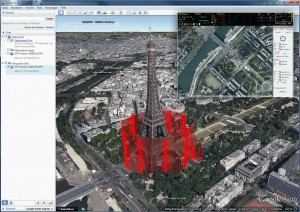 With a Circle-of-Interest-Funktion (COI) it is possible to surround an object and aim with the camera at the center. With a Circle-of-Interest-Funktion (COI) it is possible to surround an object and aim with the camera at the center.Perfect for video, documentation and 3D-measurements. | ||
| Position Save | ||
| Save a tracking shot | ||
| Relative Waypoints For applications such as panoramas or large-scale mapping you can save waypoints as relative positions to the previous waypoint – and rotate the relative position depending on the orientation of the copter. For example, go to 50 meters to the left of the present position – this will vary depending on the copter’s orientation. Relative waypoints can be preset just using the RC transmitter and without the need for a laptop or tablet. | ||
| Point of Interest (POI) 3DWaypoints For imaging ground-based features like buildings or other structures, you can program 3D waypoints around the particular point of interest and the copter will automatically turn to face the POI as it flies between the waypoint. Each waypoint is both a position and a height. | ||
| Flexible autotrigger A camera can be triggered by waypoints, time-controlled or distance-controlled. A picture every 15m, no matter the speed, is an easy task. This makes large-scale mapping child’s play. This feature can be combined with waypoint-flights -> flying all the corner points as waypoints of a given area will suffice to taking pictures with sufficient overlapping. This reduces the number of waypoints. With only 16 waypoints the same effectiveness can be achieved wherefore other systems would require hundreds of points. | ||
| Flightsimulation within the copter A flight simulator is an integrated part of the firmware of the MikroKopters. The simulation allows the user to use all the original routines within the MikroKopter. The virtual position can be observed at the PC screen and changed with the RC or with waypoints. This is ideal for testing camera shots and waypoint flights. Logfiles are created with the simulated data. Furthermore we habe a flight simulator that allows simulated flight training with the original RC. | ||
| Flight Data Logging For post-flight analysis you can log data five times a second to a micro-SD card on the Navigation Control board. This information contains numerous relevant data values including GPS-position, height, speed, voltage, position of switches, flight attitude, currents of each motor, temperature, pilot and autopilot inputs. | ||
| Take-off Weight and Payload | ||
| Automatic Camera Tilt Compensation Copter motion is automatically removed so that the actual camera angle to the ground can be changed using a control on either the pilot’s RC transmitter – or a separate RC transmitter for the camera operator. | ||
| Emergency Failsafe Recovery If the copter’s flight control receiver loses contact with the pilot’s RC transmitter, the copter will automatically return to the take-off point at a preset height chosen by the pilot. If the flight battery voltage drops below a pilot-selected threshold value, the copter will also return to the take-off point, and, if the pilot preset the option, will automatically land. | ||
| State-of-the-Art Motors The compact brushless motors we use are minimum-wear and provide high performance and a long service life. We use our own test stand to determine the efficiency of different motor/propeller combinations. | ||
| Next-Generation Brushless Motor Controller | ||
| Advanced 32-bit ARM and AVR Central Processors Depending on the number of motors, from 12 to 15 single chip microcomputers are used for flight control, navigation, motor controls, GPS, camera interface and other functions. The computer source code for these microcontrollers is Open Source, written in C, and can be modified by our customers if required. | ||
| Cutting Edge Nanoscale Sensors I | ||
| Open Interface The serial protocol for controlling and configurating the MikroKopter is open and documented. Control the Copter with your own firmware via wireless telemetry intercace or an own controller on board. | ||
| Advanced Global Positioning System The GPS board uses the most recent, highly-sensitive GPS antenna and preamplifier with a SAW frequency filter that can get a 3D position lock with a limited sky view or when satellites are shielded by terrain and buildings. This system can get positional data from the U.S. GPS, the Russian GLONASS, and the Chinese BeiDou satellites. | ||
| Telemetry via Personal Computer or Tablet Mikrokopter’s copters have a bidirectional telemetry system with a range of up to 6 Km and operating at different frequencies (2,4Ghz, 868Mhz, or 900Mhz) display copter position and operating parameters on a PC or tablet. These parameters include the copter’s height, flight battery voltage, elapsed flight time, motor currents and more. This telemetry data can be integrated with Google Earth for navigation or stored for offline use and integration with your own map data. | ||
| Voice Announcements and Logging of Telemetry Data For certain RC Transmitters such as JETI or the Graupner HoTT the transmitter can speak flight critical information out loud. This includes flight battery voltage, height, distance, mode changes, and errors. These voice announcements can be made predetermined time intervals or in response to a control switch on the RC transmitter. This telemetry data can also be logged in the RC transmitter – for example, the last GPS position in the case of a crash or loss of contact with the copter. | ||
| Long Flight Times Depending on the weight of the aircraft and the batteries being used, copter flight times can be as long as 40 minutes. We provide free software that helps you predict what likely flight times will be. | ||
| Instructor and Trainee Pilot Systems Using Graupner HoTTT transmitters and receivers, there is no need for a “buddy cable” between the instructor and the student’s transmitter – it can all happen wirelessly. Better yet, specific channels for controlling the camera and even copter yaw control can be assigned wirelessly to a second transmitter for a camera operator. | ||
| Sony Camera Controls Mikropkopters Sony LANC control allows the pilot or the camera operator to have full control of starting/stopping video recording, shooting still images, and zooming the camera lens in and out. For more informations click here | ||
| Safe and Easy Flight Operations Flying a Mikrokopter multi-rotor copter is safe and easy because we have such features as Come Home (which brings the copter home at a preset altitude), CareFree Mode (which allows beginners to fly without worrying about control reversal), Automatic take-off and landing to make learning to fly safer, Failsafe (which brings the copter home on loss of contact with the RC transmitter) and Geo-fencing (which confines the copter to specific territory). | ||
| Geo-Fencing for Safety Mikrokopter provides programmable features that create an invisible cage in the sky. When enabled the copter will never fly outside this cage and can thus remain safely in view even when a novice pilot is flying the copter. | ||
| Almost Ready-to-Fly Copters All you need do is unbox the copter, charge up some batteries and install the propellers on the copter and you are ready to fly. | ||
| Live Payload Video Downlinked to the Ground The payload camera can downlink a wireless video feed so you can watch the video either on a monitor screen or using video goggles during the flight. Click here for more details | ||
| Free Mikrokopter Software Mikrokopter provides free software updates for new features for the Flight Controller, Navigation Controller, GPS board, and the Brushless Controllers. You also get the free Configuration program, Mikrokopter Tool (for Windows PCs), an Android tablet based flight planning tool, MKTT, for setting up waypoints, and geo-fencing. We also provide a free flight simulator, AeroSimRC (the software is free, but you need to purchase a USB dongle), so that you can learn to fly a copter without expensive crashes and whatever the weather is doing outside. Finally, we also provide a free flight time calculator so you can predict your flight times, and a special tool for reviewing the GPX flight data logs created by the Navigation Control board. | ||
| Mikrokopter Avionics Are Widely Used Mikrokopter avionics boards are widely used on many different brands of copters – you may not see the Mikrokopter name, but it’s often there under the protective hoods. There are thousands of copters flying Mikrokopter avionics. | ||
| Source code Mikrokopter makes is source code available under an Open Source licenses so you can easily tailor it to your needs. Note: to compile the Navigation Control board source code you need our Lib-Link license. | ||
| Made in Germany For the past 15 years, Mikrokopter has developed its own hardware and software for the Flight Control, Navigation Control, GPS, and Brushless Controllers. We pride ourselves on high quality hardware and software. | ||
| Low-Stress Panic-Free Flying If you simply let go of the RC transmitter sticks and let them return to their center position, the MK Avionics will bring the copter to a standstill in the sky so that you can decide what you need to do next. If you operate the GPS switch, the copter will go to a preset height and then return to the take-off point automatically. | ||
| Carefree Mode for Beginners One of the hardest things for beginning pilots to master is the control reversal when the copter flies with boom #1 pointing in any direction but away from the pilot. Worst case, if boom #1 points at the pilot, all left/right control inputs must be reversed and this can easily cause a beginner to lose control and crash the copter. That’s where Carefree Mode comes in – it automatically senses where boom #1 is with respect to the pilot and allows to pilot to fly “nose out” all the time, regardless of the copter’s actual orientation. Carefree Mode can also be adjusted in flight if the pilot wants the copter to fly around to the side or behind the pilot. | ||
| Click and Fly : Single Point Navigation With just a single click or tap on a map on the screen of a PC or Android tablet you can tell the copter where to fly and autoland there. | ||
| Boat Mode : Advanced Feature This is an advanced feature that permits the pilot to initialize the solid state gyroscopes for safe flight even when the copter is resting on a moving boat. | ||
| Long Distance Waypoint Flying Mikrokopter permits waypoint flying up to 250 meters from the take-off point. If you need to pre-program more distant waypoints, all you need do is purchase an extended range license and copy the license file on to the microSD card in the Navigation Control Board. | ||
Easy Maintenance and Simple Modular Design |
xxx 'en'
xxx Slider: slider/en/supporten/features


